Table of Contents
ToggleCBSE Class 10 Science Revised Syllabus 2025
The Science curriculum for Classes IX and X (2024-25) is designed to foster cognitive, affective, and psychomotor skills, promoting inquiry, creativity, and objectivity in students. It introduces themes like Food, Materials, The World of The Living, How Things Work, Moving Things, People and Ideas, Natural Phenomena, and Natural Resources, ensuring a balanced approach without overwhelming learners. Emphasizing hands-on activities and abstract reasoning, students explore foundational concepts such as atoms, molecules, and Newton’s law of gravitation, while Physics, Chemistry, and Biology emerge as distinct disciplines. The evaluation includes an 80-mark Annual Examination and a 20-mark Internal Assessment, comprising periodic tests, diverse assessments (quizzes, projects, etc.), practical work, and a portfolio showcasing classwork and related activities. This curriculum bridges theoretical understanding with real-world applications, preparing students for advanced learning while nurturing their scientific temperament and reasoning abilities.
COURSE STRUCTURE CLASS IX
(Annual Examination) Marks: 80
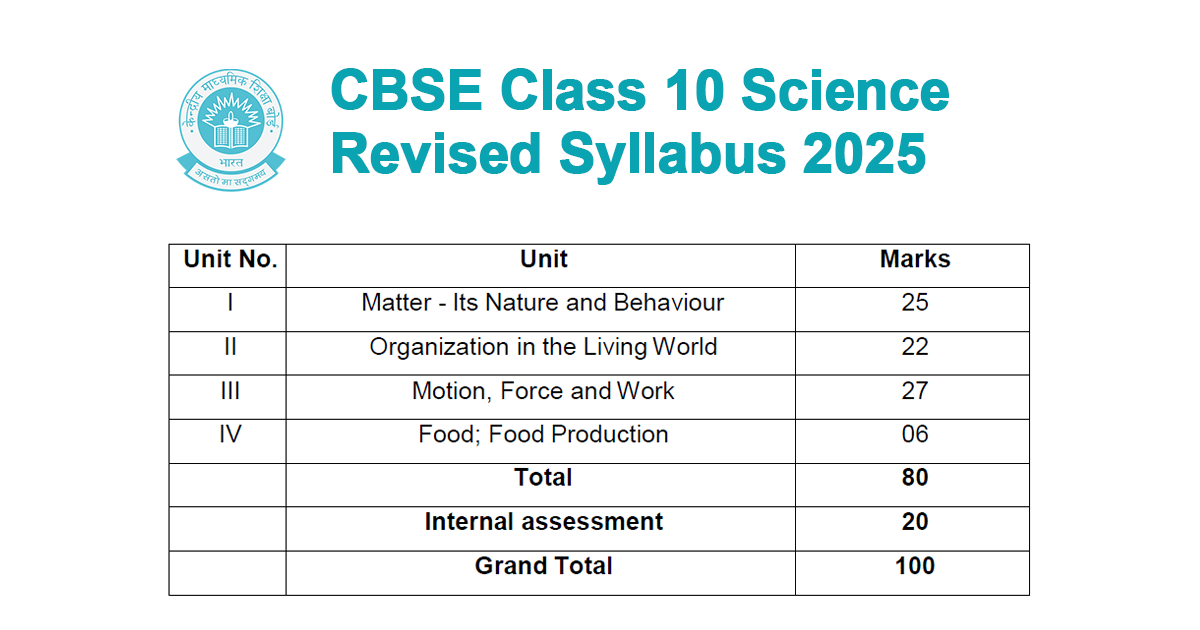
| Unit No. | Unit | Marks |
| I | Matter – Its Nature and Behaviour | 25 |
| II | Organization in the Living World | 22 |
| III | Motion, Force and Work | 27 |
| IV | Food; Food Production | 06 |
| Total | 80 | |
| Internal assessment | 20 | |
| Grand Total | 100 |
Theme: Materials
Unit I: Matter-Nature and Behaviour
Definition of matter; solid, liquid and gas; characteristics – shape, volume, density; change of state- melting (absorption of heat), freezing, evaporation (cooling by evaporation), condensation, sublimation.
Nature of matter: Elements, compounds and mixtures. Heterogeneous and homogenous mixtures, colloids and suspensions. Physical and chemical changes (excluding separating the components of a mixture).
Particle nature and their basic units: Atoms and molecules, Law of Chemical Combination, Chemical formula of common compounds, Atomic and molecular masses.
Structure of atoms: Electrons, protons and neutrons, Valency, Atomic Number and Mass Number, Isotopes and Isobars.
Theme: The World of the Living
Unit II: Organization in the Living World
Cell – Basic Unit of life : Cell as a basic unit of life; prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, multicellular organisms; cell membrane and cell wall, cell organelles and cell inclusions; chloroplast, mitochondria, vacuoles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus; nucleus, chromosomes – basic structure, number.
Tissues, Organs, Organ System, Organism:
Structure and functions of animal and plant tissues (only four types of tissues in animals; Meristematic and Permanent tissues in plants).
Theme: Moving Things, People and Ideas
Unit III: Motion, Force and Work
Motion: Distance and displacement, velocity; uniform and non-uniform motion along a straight line; acceleration, distance-time and velocity-time graphs for uniform motion and uniformly accelerated motion, elementary idea of uniform circular motion.
Force and Newton’s laws : Force and Motion, Newton’s Laws of Motion, Action and Reaction forces, Inertia of a body, Inertia and mass, Momentum, Force and Acceleration.
Gravitation: Gravitation; Universal Law of Gravitation, Force of Gravitation of the earth (gravity), Acceleration due to Gravity; Mass and Weight; Free fall.
Floatation: Thrust and Pressure. Archimedes’ Principle; Buoyancy.
Work, Energy and Power: Work done by a Force, Energy, power; Kinetic and Potential energy; Law of conservation of energy (excluding commercial unit of Energy).
Sound: Nature of sound and its propagation in various media, speed of sound, range of hearing in humans; ultrasound; reflection of sound; echo.
Theme: Food
Unit IV: Food Production
Plant and animal breeding and selection for quality improvement and management; Use of fertilizers and manures; Protection from pests and diseases; Organic farming.
Note for the Teachers:
- The chapter Natural Resources (NCERT Chapter 14) will not be assessed in the year-end However, learners may be assigned to read this chapter and encouraged to prepare a brief write up on any concept of this chapter in their Portfolio. This may be for Internal Assessment and credit may be given for Periodic Assessment/Portfolio.
- The NCERT text books present information in boxes across the These help students to get conceptual clarity. However, the information in these boxes would not be assessed in the year-end examination.
PRACTICALS
Practicals should be conducted alongside the concepts taught in theory classes.
(LIST OF EXPERIMENTS)
- Preparation of: Unit-I
- a true solution of common salt, sugar and alum
- a suspension of soil, chalk powder and fine sand in water
- a colloidal solution of starch in water and egg albumin/milk in water and distinguish between these on the basis of
- transparency
- filtration criterion
- stability
- Preparation of Unit-I
- A mixture
- A compound
- using iron filings and sulphur powder and distinguishing between these on the basis of:
- appearance, e., homogeneity and heterogeneity
- behaviour towards a magnet
- behaviour towards carbon disulphide as a solvent
- effect of heat
- Perform the following reactions and classify them as physical or chemical changes: Unit-I
- Iron with copper sulphate solution in water
- Burning of magnesium ribbon in air
- Zinc with dilute sulphuric acid
- Heating of copper sulphate crystals
- Sodium sulphate with barium chloride in the form of their solutions in water
- Preparation of stained temporary mounts of (a) onion peel, (b) human cheek cells & to record observations and draw their labeled diagrams. Unit-II
- Identification of Parenchyma, Collenchyma and Sclerenchyma tissues in plants, striped, smoothand cardiac muscle fibers and nerve cells in animals, from prepared slides. Draw their labeled Unit-II
- Determination of the melting point of ice and the boiling point of Unit-I
- Verificationof the Laws of reflection of Unit-III
- Determination of the density of solid (denser than water) by using a spring balance and a measuring Unit-III
- Establishing the relation between the loss in weight of a solid when fully immersed in Unit-III
- Tap water
- Strongly salty water with the weight of water displaced by it by taking at least two
- Determination of the speed of a pulse propagated through a stretched string/slinky (helical spring). Unit-III
- Verification of the law of conservation of mass in a chemical Unit-III
COURSE STRUCTURE CLASS X
(Annual Examination)
Marks: 80
| Unit No. | Unit | Marks |
| I | Chemical Substances-Nature and Behaviour | 25 |
| II | World of Living | 25 |
| III | Natural Phenomena | 12 |
| IV | Effects of Current | 13 |
| V | Natural Resources | 05 |
| Total | 80 | |
| Internal assessment | 20 | |
| Grand Total | 100 |
Theme: Materials
Unit I: Chemical Substances – Nature and Behaviour
Chemical reactions: Chemical equation, Balanced chemical equation, implications of a balanced chemical equation, types of chemical reactions: combination, decomposition, displacement, double displacement, precipitation, endothermic exothermic reactions, oxidation and reduction.
Acids, bases and salts: Their definitions in terms of furnishing of H+ and OH– ions, General properties, examples and uses, neutralization, concept of pH scale (Definition relating to logarithm not required), importance of pH in everyday life; preparation and uses of Sodium Hydroxide, Bleachingpowder, Baking soda, Washing soda and Plaster of Paris.
Metals and nonmetals: Properties of metals and non-metals; Reactivity series; Formation and properties of ionic compounds; Basic metallurgical processes; Corrosion and its prevention.
Carbon compounds: Covalent bonding in carbon compounds. Versatile nature of carbon. Homologous series. Nomenclature of carbon compounds containing functional groups (halogens, alcohol, ketones, aldehydes, alkanes and alkynes), difference between saturated hydro carbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Chemical properties of carbon compounds (combustion, oxidation, addition and substitution reaction). Ethanol and Ethanoic acid (only properties and uses), soaps and detergents.
Theme: The World of the Living
Unit II: World of Living
Life processes: ‘Living Being’. Basic concept of nutrition, respiration, transport and excretion in plants and animals.
Control and co-ordination in animals and plants: Tropic movements in plants; Introduction of plant hormones; Control and co-ordination in animals: Nervous system; Voluntary, involuntary and reflex action; Chemical co-ordination: animal hormones.
Reproduction: Reproduction in animals and plants (asexual and sexual) reproductive health – need and methods of family planning. Safe sex vs HIV/AIDS. Child bearing and women’s health.
Heredity and Evolution: Heredity; Mendel’s contribution- Laws for inheritance of traits: Sex determination: brief introduction: (topics excluded – evolution; evolution and classification and evolution should not be equated with progress).
Theme: Natural Phenomena
Unit III: Natural Phenomena
Reflection of light by curved surfaces; Images formed by spherical mirrors, centre of curvature, principal axis, principal focus, focal length, mirror formula (Derivation not required),magnification.
Refraction; Laws of refraction, refractive index.
Refraction of light by spherical lens; Image formed by spherical lenses; Lens formula (Derivation not required); Magnification. Power of a lens.
Functioning of a lens in human eye, defects of vision and their corrections, applications of spherical mirrors and lenses.
Refraction of light through a prism, dispersion of light, scattering of light, applications in dailylife (excluding colour of the sun at sunrise and sunset).
Theme: How Things Work
Unit IV: Effects of Current
Electric current, potential difference and electric current. Ohm’s law; Resistance, Resistivity, Factors on which the resistance of a conductor depends. Series combination of resistors, parallel combination of resistors and its applications in daily life. Heating effect of electric current and its applications in daily life. Electric power, Interrelation between P, V, I and R.
Magnetic effects of current: Magnetic field, field lines, field due to a current carrying conductor, field due to current carrying coil or solenoid; Force on current carrying conductor, Fleming’s Left Hand Rule, Direct current. Alternating current: frequency of AC. Advantage of AC over DC. Domestic electric circuits.
Theme: Natural Resources
Unit V: Natural Resources
Our environment: Eco-system, Environmental problems, Ozone depletion, waste production and their solutions. Biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances.
Note for the Teachers:
- The chapter Management of Natural Resources (NCERT Chapter 16) will not be assessed in the year-end examination. However, learners may be assigned to read this chapter and encouraged to prepare a brief write up to any concept of this chapter in their Portfolio. This may be for Internal Assessment and credit may be given Periodic Assessment/Portfolio).
- The NCERT text books present information in boxes across the book. These help students to get conceptual clarity. However, the information in these boxes would not be assessed in the year-end
PRACTICALS
Practical should be conducted alongside the concepts taught in theory classes.
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
- Finding the pH of the following samples by using pH paper/universal indicator: Unit-I
- Dilute Hydrochloric Acid
- Dilute NaOH solution
- Dilute Ethanoic Acid solution
- Lemon juice
- Water
- Dilute Hydrogen Carbonate solution
- Studying the properties of acids and bases (HCl & NaOH) on the basis of their reaction with: Unit-I
- Litmus solution (Blue/Red)
- Zinc metal
- Solid sodium carbonate
- Performing and observing the following reactions and classifying them into: Unit-I
- Combination reaction
- Decomposition reaction
- Displacement reaction
- Double displacement reaction
- Action of water on quicklime
- Action of heat on ferrous sulphate crystals
- Iron nails kept in copper sulphate solution
- Reaction between sodium sulphate and barium chloride solutions
- Observing the action of Zn, Fe, Cu and Al metals on the following salt solutions: Unit-I
- ZnSO4(aq)
- FeSO4(aq)
- CuSO4(aq)
- Al2 (SO4)3(aq)
Arranging Zn, Fe, Cu and Al (metals) in the decreasing order of reactivity based on the above result.
- Studying the dependence of potential difference (V) across a resistor on the current (I) passing through it and determine its Also plotting a graph between V and I. Unit-IV
- Determination of the equivalent resistance of two resistors when connected in series and Unit-IV
- Preparing a temporary mount of a leaf peel to show Unit- II
- Experimentally show that carbon dioxide is given out during Unit-II
- Study of the following properties of acetic acid (ethanoic acid): Unit- I
- Odour
- solubility in water
- effect on litmus
- reaction with Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate
- Study of the comparative cleaning capacity of a sample of soap in soft and hard water. Unit- I
- Determination of the focal length of: Unit-III
- Concave mirror
- Convex lens by obtaining the image of a distant
- Tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for different angles of Measure the angle of incidence, angle of refraction, angle of emergence and interpret the result. Unit – III
- Studying (a) binary fission in Amoeba, and (b) budding in yeast and Hydra with the help of prepared Unit-II
- Tracing the path of the rays of light through a glass Unit-III
- Identification of the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed (Pea, gram or red kidney bean). Unit-II
Download PDF File : Click Here
PRESCRIBED BOOKS:
- Science-Textbook for class IX-NCERT Publication
- Science-Text book for class X- NCERT Publication
- Assessment of Practical Skills in Science-Class IX – CBSE Publication
- Assessment of Practical Skills in Science- Class X- CBSE Publication
- Laboratory Manual-Science-Class IX, NCERT Publication
- Laboratory Manual-Science-Class X, NCERT Publication
- Exemplar Problems Class IX – NCERT Publication
- Exemplar Problems Class X – NCERT Publication
Theory (80 marks) Question Paper Design
(Class X)
Subject: Science
| Competencies | Total |
| Demonstrate Knowledge and Understanding | 46 % |
| Application of Knowledge/Concepts | 22 % |
| Formulate, Analyze, Evaluate and Create | 32 % |
| 100% |
Note:
- Typology of Questions: VSA including objective type questions, Assertion – Reasoning type questions; SA; LA; Source-based/ Case-based/ Passage-based/ Integrated assessment
- An internal choice of approximately 33% would be
Internal Assessment (20 Marks)
- Periodic Assessment – 05 marks + 05 marks
- Subject Enrichment (Practical Work) – 05 marks
- Portfolio – 05 marks
Suggestive verbs for various competencies
- Demonstrate Knowledge and Understanding
- State, name, list, identify, define, suggest, describe, outline, summarize,
- Application of Knowledge/Concepts
- Calculate, illustrate, show, adapt, explain, distinguish,
- Formulate, Analyze, Evaluate and Create
- Interpret, analyze, compare, contrast, examine, evaluate, discuss, construct,
Read Also : CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Revised Syllabus 2025 – Download Latest Updates
Read Also : Google Internship Programme in Public Sector Security Architecture 2025